Description
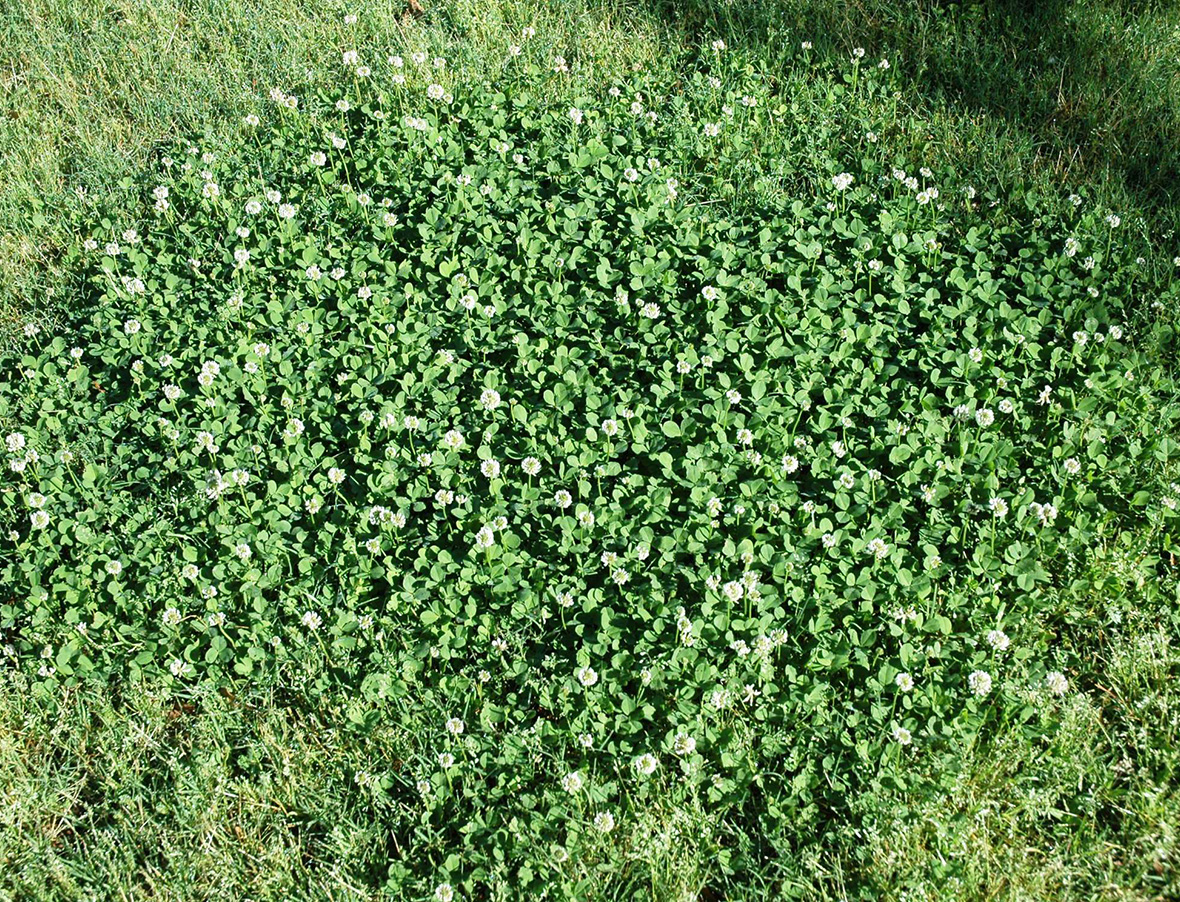
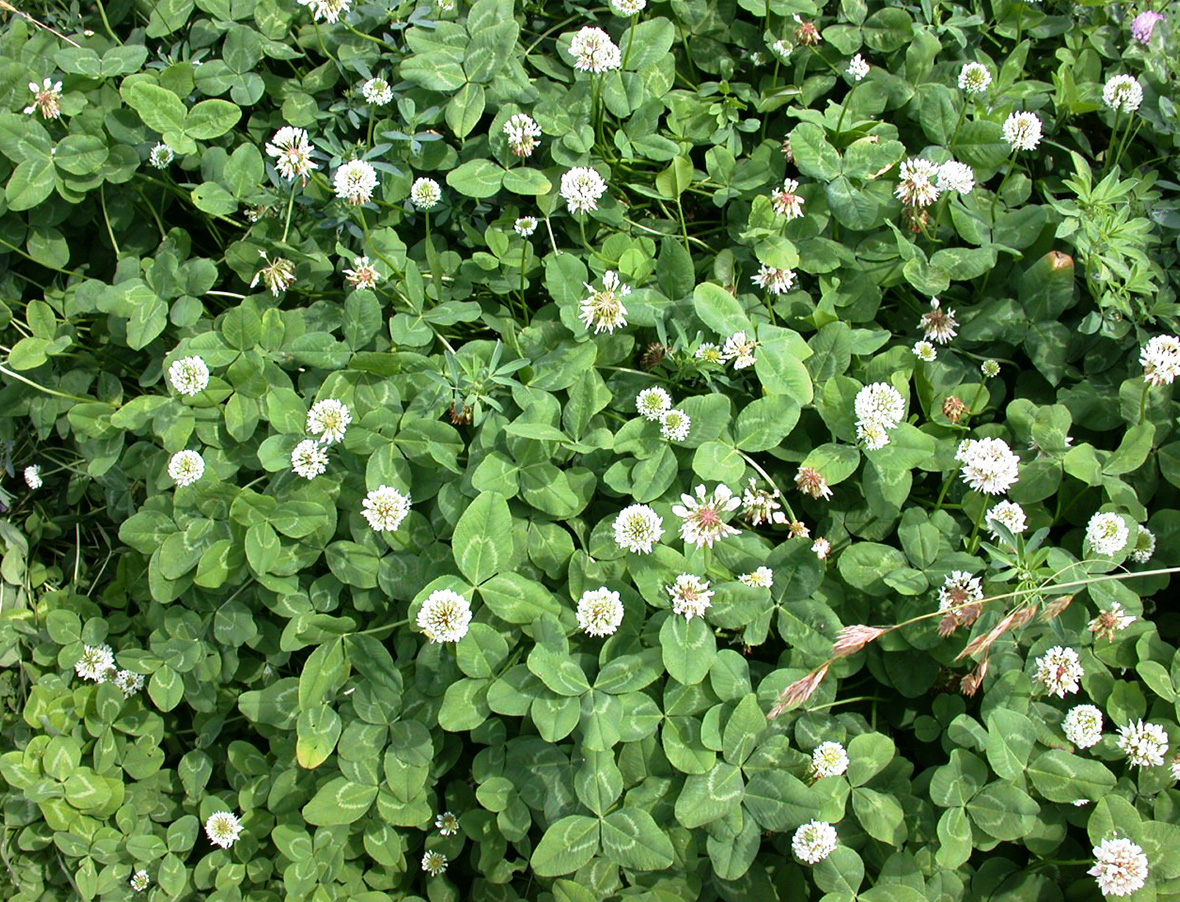
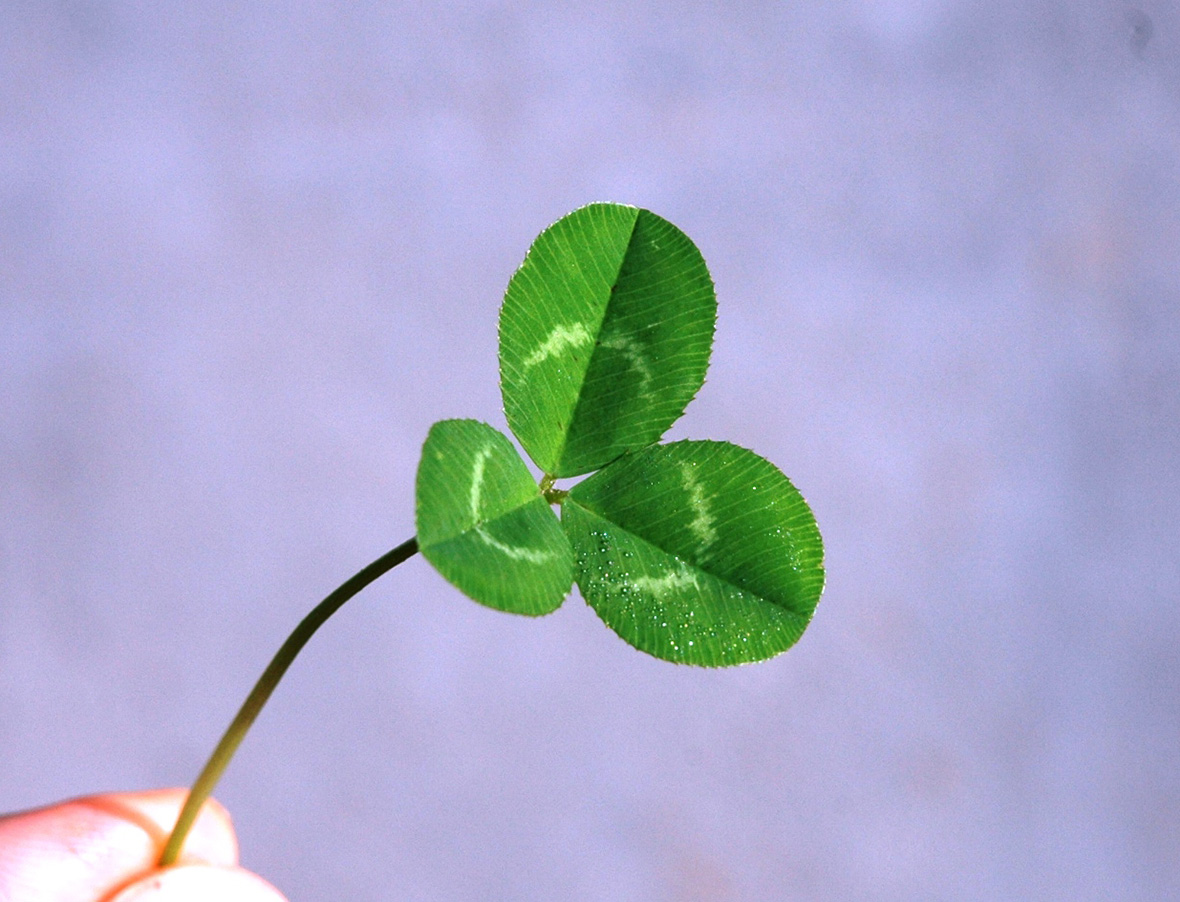
White clover, found throughout the United States, is a shallow rooted winter perennial legume which spreads by stolons or above ground runners. The plant takes root from the stolons at nodes along the stems when they come in contact with the soil. The white clover plant has compound leaves divided into three leaflets which are all joined at a central point and originate at the nodes along the stems.
Leaves may contain a white 'watermark'. White clover is adapted to many soils but tends to grow best in soils that are moist and low in nitrogen. The flowers are an aggregate of 20 to 40 individual flowers. They are white in color, although some have a slight pink tint. White clover flowers from May through September.
Weed Photos: Courtesy of Dr. Lambert McCarty. Clemson University. Clemson, SC.
Herbicide Use
Knowing the optimum timing for a chemical control application will help to minimize the amount of chemical required for white clover control. Control will be reduced when the plant is flowering. The best timing for a chemical application for clover control is in the fall. Being a winter perennial, active growth from germinating seeds or existing plants begins with cooler temperatures and increased moisture. Active growth continues in until night temperatures reach freezing. Growth resumes in the spring with increases in temperature. For optimum control, make your herbicide application when white clover is actively growing and in the second trifoliolate leaf to flower stage of growth. Spring applications are most effective after night temperatures are consistently about 50 degrees. More active ingredient may be required for spring clover control.
Distribution
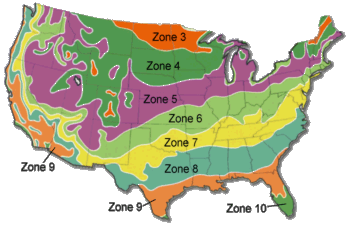
Germination Dates
Recommendations
PowerZone® Broadleaf Herbicide
Q4® Plus Turf Herbicide for Grassy & Broadleaf Weeds
SpeedZone® Broadleaf Herbicide for Turf
SpeedZone® Southern Broadleaf Herbicide for Turf
SpeedZone® Southern EW Broadleaf Herbicide for Turf
Super Trimec® Broadleaf Herbicide
Surge® Broadleaf Herbicide for Turf
Trimec® 1000 Low Odor Broadleaf Herbicide
Trimec® 992 Broadleaf Herbicide
Trimec® Bentgrass Formula Broadleaf Herbicide
Trimec® Classic Broadleaf Herbicide
Trimec® Encore® Broadleaf Herbicide
Trimec® Southern Broadleaf Herbicide for Sensitive Southern Grasses
TZone SE Broadleaf Herbicide for Tough Weeds






