Description
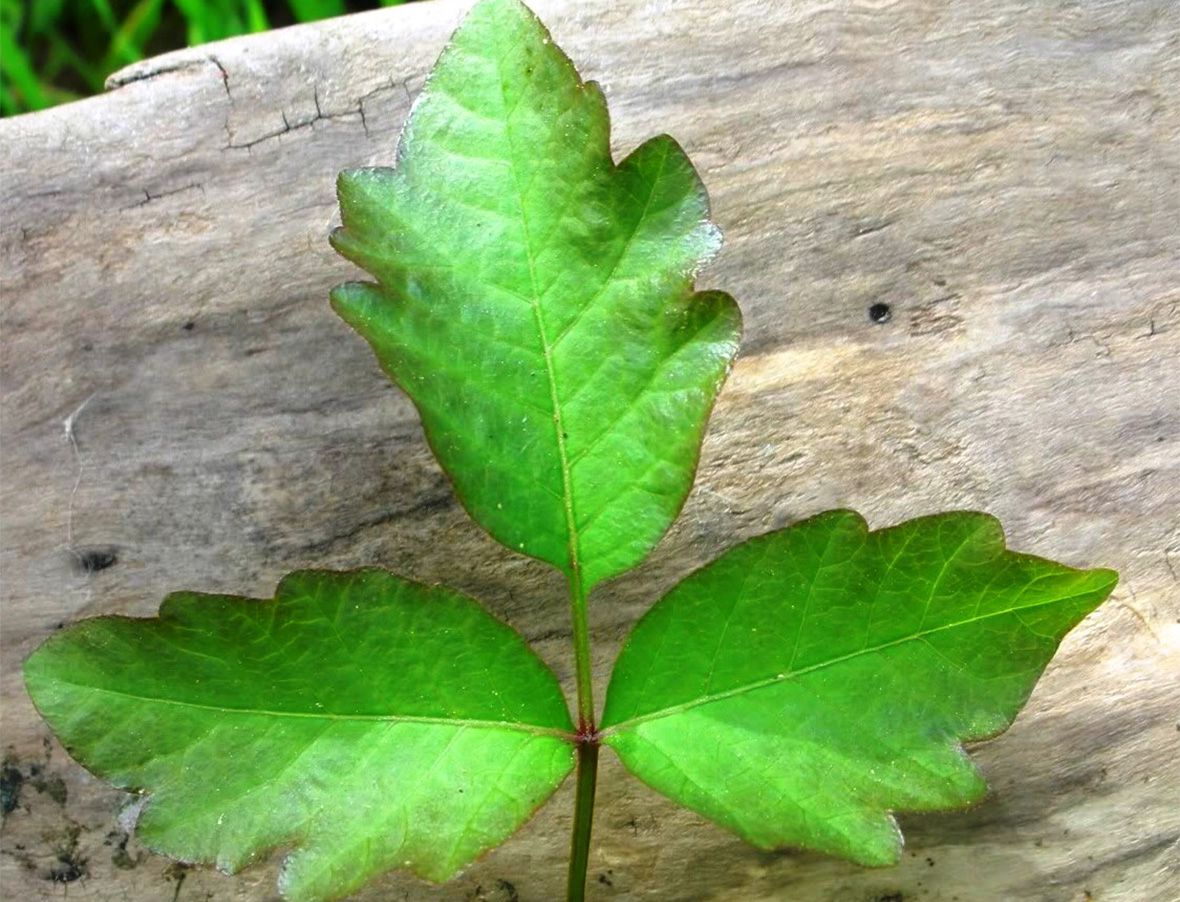
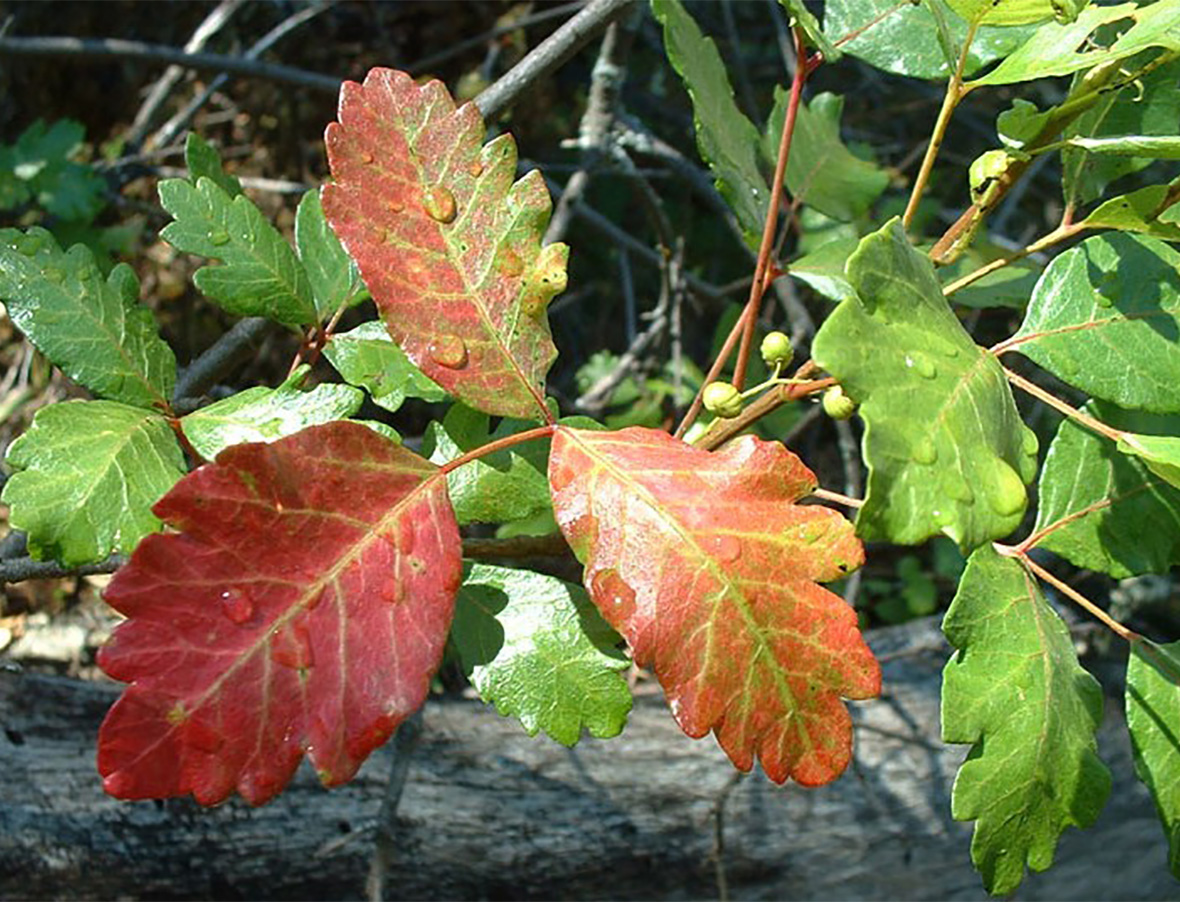
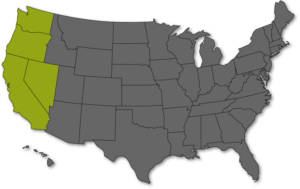
Poison oak is identified by 1-inch to 3-inch long leaflets with two to seven deep lobes resembling oak leaves. Lateral leaflets appear without stalks on viny stems about 3 to 4 feet tall. Like poison ivy, leaflets are grouped three per leaf, and flowers are yellowish. Poison oak is found throughout the southeast and along the Pacific coast in the United States.
Weed Photos: Courtesy of Dr. Lambert McCarty. Clemson University. Clemson, SC.
Herbicide Use
Large, well-established infestations can be a problem to remove either mechanically or chemically. A series of post-emergence broadleaf herbicide foliar treatments may be required to conquer a large infestation of poison ivy or poison oak. Vines which have become well-established in trees can be practically impossible to eradicate without herbicide damage to the tree. In these situations, an ester herbicide labeled for mixing with oil for a basal stem treatment may be required. For optimum foliar control, make your herbicide application to poison oak that is actively growing and in the first trifoliate leaf to flower stage of growth.
Distribution
Germination Dates
Recommendations
PowerZone® Broadleaf Herbicide
Q4® Plus Turf Herbicide for Grassy & Broadleaf Weeds
SpeedZone® Broadleaf Herbicide for Turf
SpeedZone® Southern Broadleaf Herbicide for Turf
SpeedZone® Southern EW Broadleaf Herbicide for Turf
Super Trimec® Broadleaf Herbicide
Surge® Broadleaf Herbicide for Turf
Trimec® 1000 Low Odor Broadleaf Herbicide
Trimec® 992 Broadleaf Herbicide
Trimec® Bentgrass Formula Broadleaf Herbicide
Trimec® Classic Broadleaf Herbicide
Trimec® Encore® Broadleaf Herbicide
Trimec® Southern Broadleaf Herbicide for Sensitive Southern Grasses
TZone SE Broadleaf Herbicide for Tough Weeds





