Description
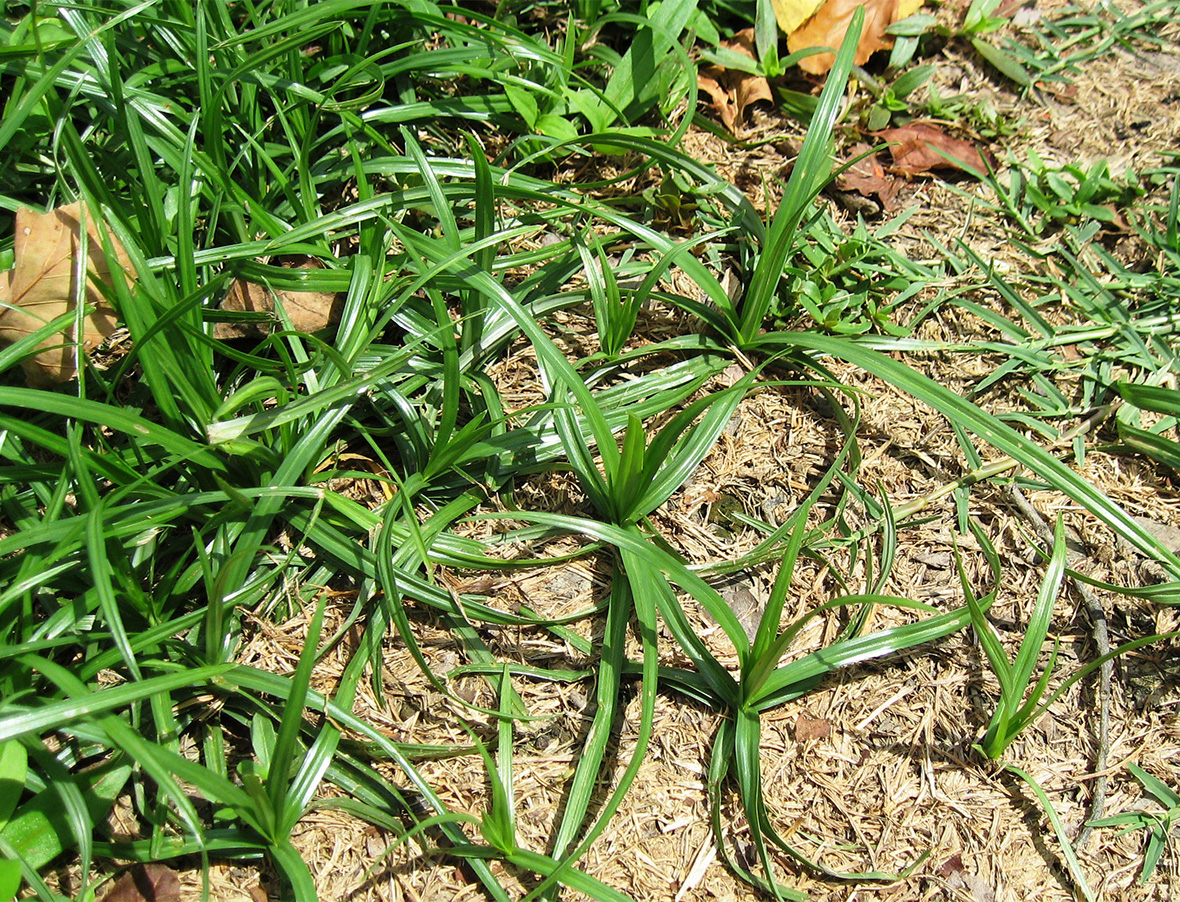
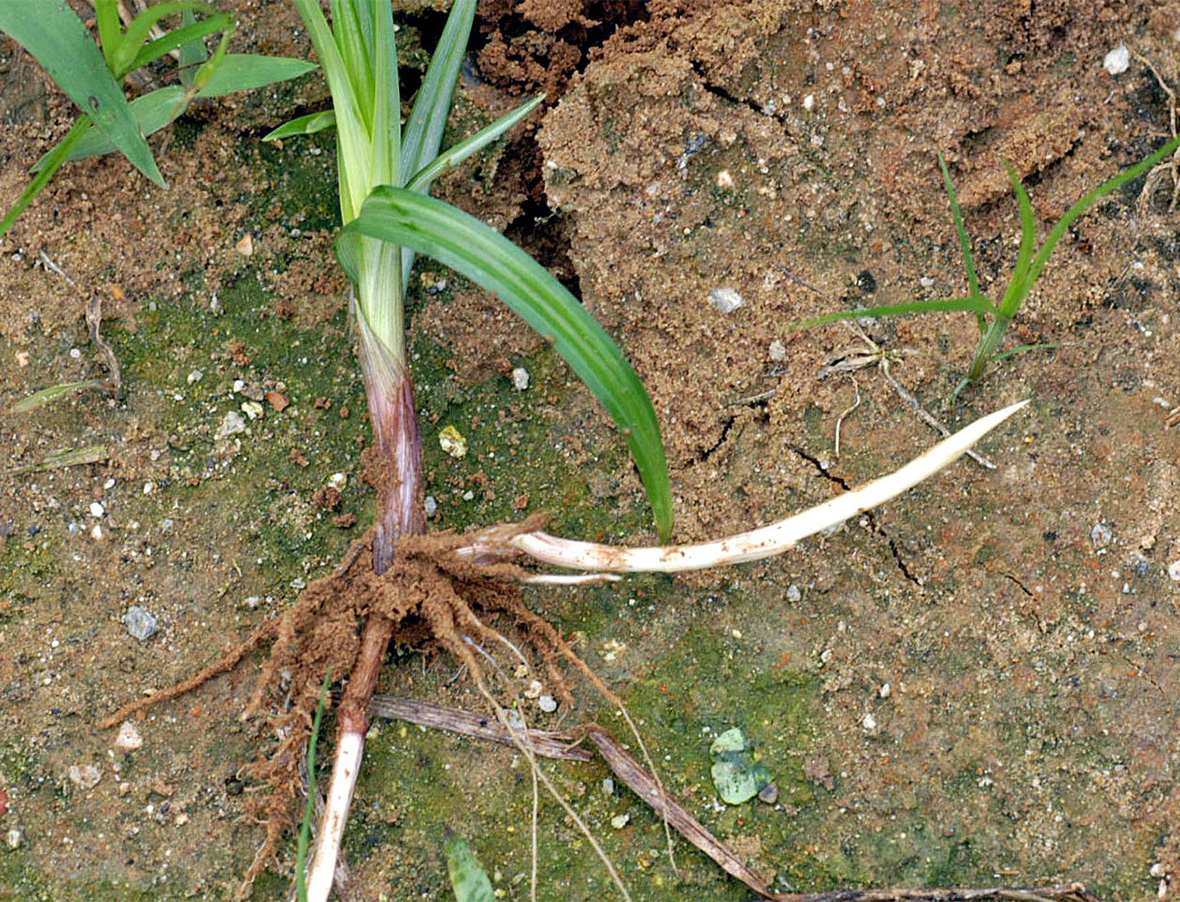
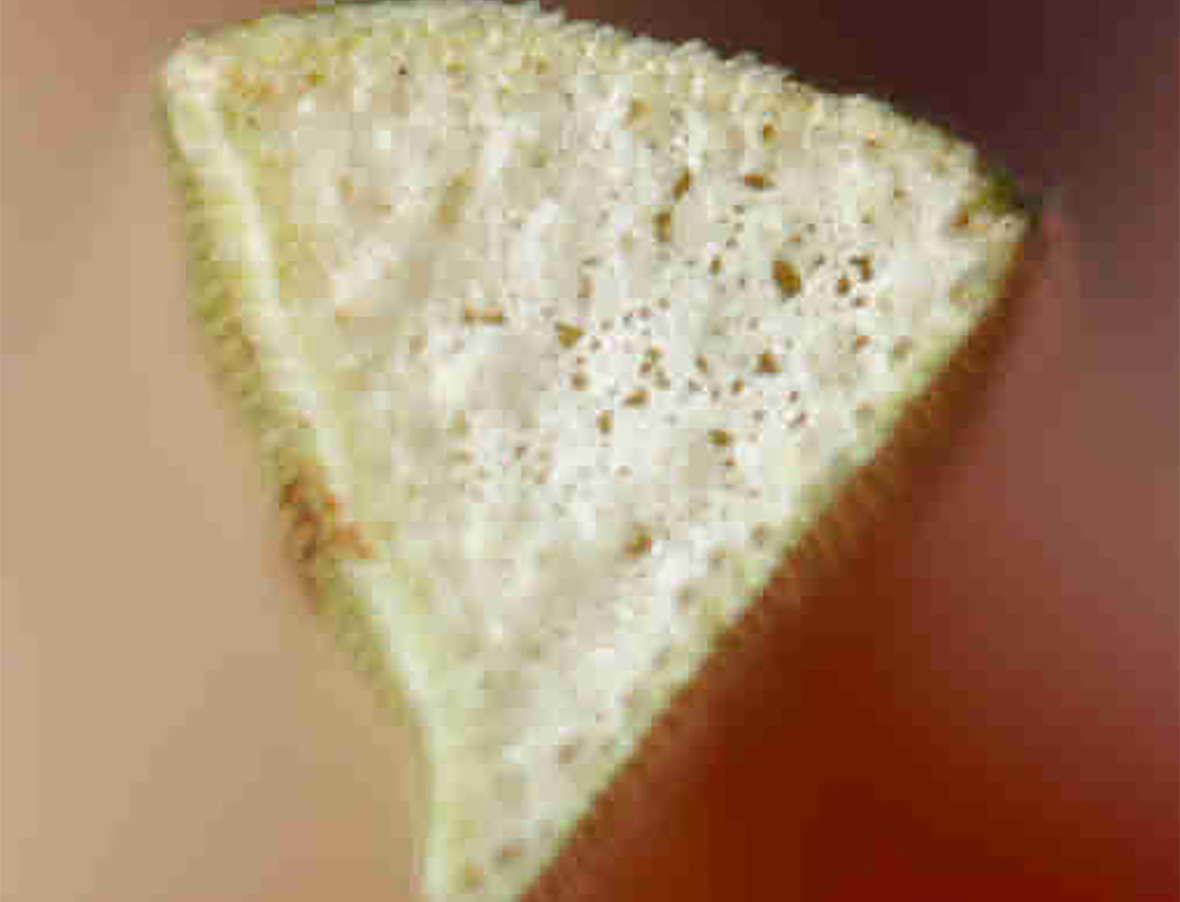
Sedges have triangular stems with waxy grass-like leaves which alternate. Sedges are not grass plants, but seedlings may be mistaken for grass. The leaves on both sedges are waxy and have an upright growth habit and a prominent midrib. Both sedges have underground root systems containing rhizomes and underground tubers which accomplish most of the reproduction. On yellow nutsedge, the tubers (nutlets) form at the end of whitish rhizomes. Purple nutsedge forms chains of tubers along brownish rhizomes. The flowers of yellow nutsedge are yellowish; the seedhead color of purple nutsedge is red-purple to brown. Both seedheads are on triangular stems. Both spread mainly by germinating underground tubers, which are the only part of the plant that over-winters. A yellow nutsedge tuber can produce 1,900 plants and 7,000 new tubers in a single growing season. Sedges do well where soil has poor drainage. Yellow nutsedge is found throughout the United States; Purple nutsedge is primarily found in the warm humid southern states.
Weed Photos: Courtesy of Dr. Lambert McCarty. Clemson University. Clemson, SC.
Herbicide Use
Use a post-emergence herbicide when nutsedge is actively growing. For best control results, time applications for nutsedge that is in the three-leaf to flower growth stage.
Distribution
Germination Dates